Browser-Based Apps
Browsers are a very restricted environment to work in, with limited options for external communications (websockets, Web Transport API, WebRTC), mixed content restrictions (HTTPS-only), and no access to the file system or any syscalls. These aside, the main issue when trying to capture traffic and send it via a different transport - such as the Mixnet - is the lack of access to browser TLS negotiation from JS or the CA certificate store.
This means that the functionality offered by our current browser-based solutions are quite restricted / specific. There are currently two options for interacting with the Mixnet from the browser: mixFetch, and the WASM SDK.
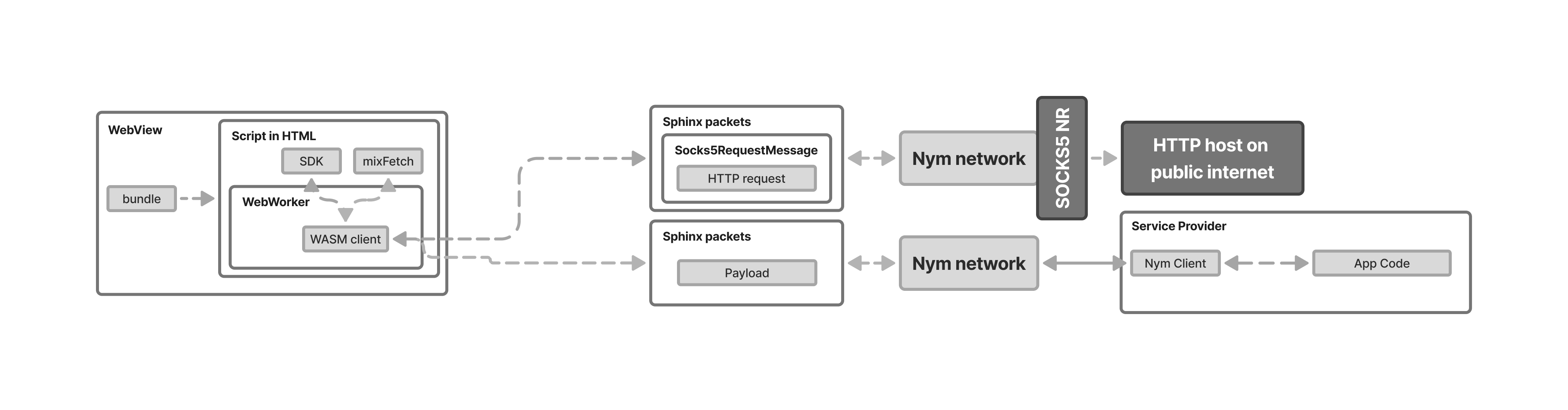
Both mixFetch and the WASM client are delivered to the client bundled into a web application.
mixFetch
Drop-in replacement for browser's fetch API that makes HTTP(S) requests via Exit Gateways using the SOCKS Network Requester.
Uses an embedded CA certificate store to establish TLS session between mixFetch and the remote host, creating a client-host secure channel from the browser to the host over the Mixnet.
Internally it uses the WASM client.
WASM Client
Makes Sphinx packets and cover traffic using WASM and sent over a Websocket to the Entry Gateway and receive responses.
This only works in messaging mode (i.e. messages sent either as text or binary data), and currently doesn’t support making IP packets that are routed to the Internet by an Exit Gateway IPR, nor does it currently expose any stream-like API. If you want to send HTTP(S) requests, use mixFetch.
Note that the limitations of CSPs and Mixed Content restrictions (i.e HTTPS only) apply to the Websocket connection as normal in browsers or embedded WebViews.
Runs in a web worker to leave UI thread free for the user.